Chances are you’ve heard the term “bitcoin mining” and your mind has started to wander towards the Western fantasy of pickaxes, dirt and striking it rich. As it turns out, that comparison isn’t too far off.
Mining bitcoin is less attractive. But equally, bitcoin mining is done by high-powered computers capable of solving complex mathematical problems. (That is, so complex that they cannot be solved by hand. The luck and work required by a computer to fix one of these problems is the equivalent of gold mined in the ground – while digging in the sand. At the time of writing, the computer’s chance of solving one of these problems is about 1 in 13 trillion, but more on that later.
The result of “bitcoin mining” is twofold. First, when computers solve these complex mathematical problems in the Bitcoin network, they produce new bitcoins. Secondly, through solving computer math problems, bitcoin miners make bitcoin payment networks reliable and secure by verifying transaction data.
There is a good chance, all of which means a lot, to explain Bitcoin mining methods in more detail, let’s start with a process that is closer to home: the regulations of the printed currency.
Bitcoin Fundamentals: How Bitcoin Differs From Traditional Currency
Consumers are more likely to trust printed currencies, at least in the United States, because the central bank backed dollar is known as the Federal Reserve In addition to a host of other responsibilities, the Federal Reserve regulates the production of new money and the government prosecutes the use of counterfeit currency.
Even digital payments using US dollars are backed by a central authority, when you make an online purchase using your debit or credit card, for example, the transaction is processed by a payment processing company. money like Mastercard or Visa. In addition to recording your transaction history, those companies insist that the transaction was not fraudulent, which is one reason your debit or credit card may be suspended while traveling.
Bitcoin, on the other hand, is not regulated by a central authority. Bitcoin is backed by millions of computers around the world called “nodes.” This computer network performs the same functions as the Federal Reserve, Visa, and Mastercard, but has A slight key difference, nodes store information about previous transactions and help verify their authenticity, unlike those central authorities, however, Bitcoin nodes are spread out all over the world and records transactions in a list of cryptocurrencies. The public can be accessed by anyone even you.
Bitcoin Basics: Cryptocurrency Mining What is it?
When someone makes a purchase or sale using bitcoin, we call it a “transaction.” Transactions made in-store and online are recorded by banks, point-of-sale systems, and physical receipts. Bitcoin miners achieve the same results. Together without these institutions, by bundling transactions in “blocks” and adding them to a public record known as “blockchain“, nodes keep records of those blocks so they can be audited in the future.
When bitcoin miners add new blocks of transactions to the blockchain, part of their job is to make sure those transactions are valid (more on the magic of what happens in a second). Bitcoin ensures that Bitcoin will not be duplicated which is the identity of the digital currency known as “duplicate spending.” With printed currency, duplicate money will not be an issue when you spend $20 at a merchant. That bill would be in the hands of employees with cryptocurrencies, however, it was a different story.
Digital data can be duplicated relatively easily, so with Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies there is a risk that a machine user can make a copy of their bitcoin and send it to someone else while still holding the original. Let’s go back and use it. The currency that was printed for a while said that someone was trying to copy the $20 bill to use both the real and the fake at the grocery store. Bills If the numbers are equal, the clerk knows that the money is duplicated, this analogy is similar to what Bitcoin miners do when verifying new transactions.
Miner Prize
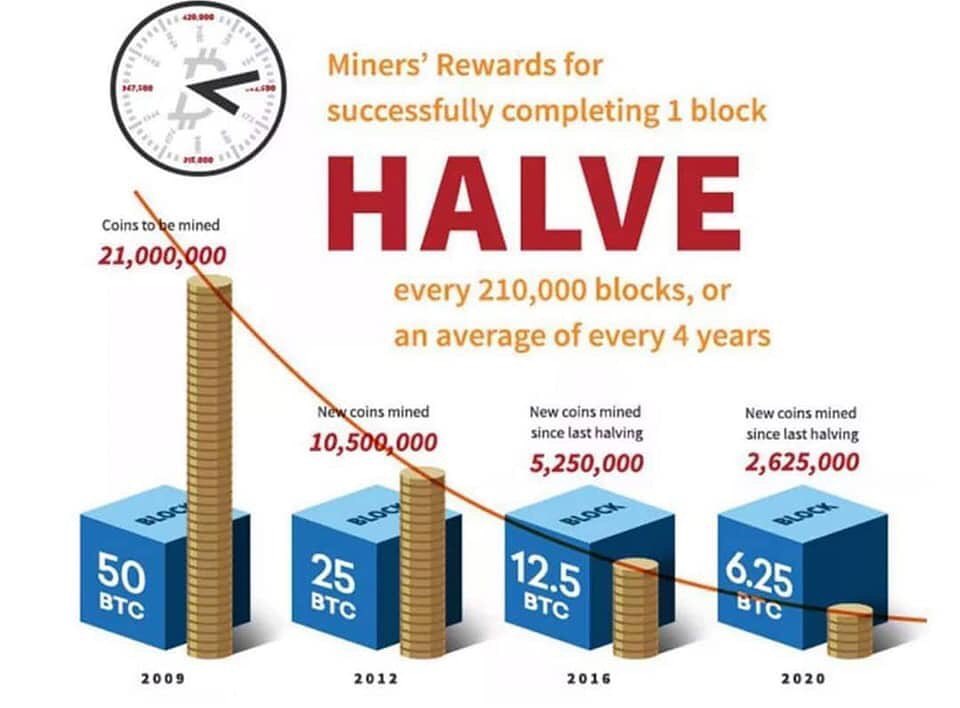
With 500,000 purchases and sales occurring in a single day, however, verifying each and every transaction can be a huge task for miners, given another major difference between Bitcoin miners and cryptocurrency miners. Federal Reserve, Mastercard or Visa. As a compensation for their efforts, miners receive bitcoin whenever they add a new block of transactions to the blockchain. The number of new bitcoins released with each mined block is known as ” The block reward” will halve every 210,000 blocks, or approximately every 4 years. In 2009 it was 50, in 2013 it was 25, in 2018 it was 12.5, and sometime in mid-2020 it dropped to 6.25.
At the halving rate, all bitcoins in circulation are approaching the limit of 21 million, making the currency rarer and more valuable over time. But it is more costly for miners.
Bi MiningHow does tcoin work?
Here’s the catch: In order for Bitcoin miners to actually earn Bitcoin by verifying two transactions, they first have to verify a 1 megabyte (MB) value of the transaction, which could theoretically be as small as 1. transactions, but there are often thousands depending on how much data each transaction stores, here’s the easy part.
Secondly, to add a transaction block to the blockchain, miners have to solve a complex mathematical problem known as the What they’re actually doing is trying to come up with a 64 hexadecimal digit called a “hash” that is less than or equal to the target hash. per second (MH/s), gigahashes per second (GH/s), or even terahashes per second (TH/s), depending on the guesswork units, all 64-digits until the exit.
The difficulty level of the latest blog at the time of writing is over. That’s the chance of a computer generating a hash below target is 1 in 13 trillion. Choosing the right hash in one try Luckily mining computer systems spit out more hash possibilities, however mining for bitcoin requires a lot of energy and sophisticated rigs.
The difficulty level will be adjusted every 2016 block or roughly every 2 weeks with the goal of keeping the mining rate constant, i.e. the more miners compete to find a solution, the more difficult it will be. If computing power is removed from the network, the difficulty will be reduced to make mining easier.
Explain like me five. (ELI5)
Here are some useful comparisons to consider:
“Say I told three friends that I was working on a number between 1 and 100 and I wrote that number on a piece of paper and sealed it in an envelope. My friends didn’t have to guess the exact number. They just It has to be the first person to guess any number less than or equal to the number I am thinking of, and there is no limit to how many times I can guess.
“Let’s say I’m thinking about the number 19. If Friend A guesses 21, they lose because 21>19. If Friend B guesses 16 and Friend C guesses 12, then they both come to a valid answer because 16 < 19 and 12 < 19. . There is no ‘extra credit’ for Friend B even though B’s answer is close to 19’s target answer.
“Now imagine I’m asking a question. But I’m not just asking for three friends and I’m not coming up with a number between 1 and 100, I’m asking for a large number. Will be a miner and I think 64 hexadecimal digits now you will see that it is very difficult to guess the correct answer.”
How can you compete with millions of players?
If 1 in 13 trillion sounds not loud enough, here’s the catch. But they also have to be the first to do so.
Since Bitcoin mining is so predictable, arriving at the correct answer before any other miner has almost everything your computer would be capable of generating hashes so quickly ten years ago. Bitcoin mining can be done on regular desktop computers, over time miners have realized that graphics cards commonly used for video games are more powerful than desktop and graphics processing units (GPUs) for mining. In 2013, Bitcoin miners started using computers designed specifically for mining. cryptocurrency As efficient as possible, this is called an application-specific integrated circuit. (ASIC) These can run from hundreds of dollars to tens of thousands, on the other hand indicating that the current price of bitcoin as of this writing is around And the reward for completing the block is 12.
Today, Bitcoin mining is so competitive that it can only be profitable by the most modern ASICs when using desktop computers, GPUs, or older ASICs than their consumption costs.Power consumption is higher than actual revenue, even with the newest unit at your disposal, one computer is hardly enough to compete with what miners call “miners.”
A mining pool is a group of miners that combine computational power and split the bitcoin mined among participants. A disproportionately large number of blocks were mined by pools than by individual miners.At some point in bitcoin’s history, a mining pool. And companies have represented 80% to 90% of bitcoin computing power.
Is Bitcoin mining sustainable?
With odds between 1 in 13 trillion difficulty levels and a large network of users verifying transactions, one block of transactions is verified every 10 minutes, but it’s important to remember that 10 minutes is goals are not rules
The bitcoin network can process about seven transactions per second, with transactions being recorded on the blockchain every 10 minutes. For comparison, Visa can process about 24,000 transactions per second, while the network of bitcoin users continues to grow. Made in 10 minutes will eventually exceed the number of transactions that can be processed in 10 minutes, at which point the transaction wait time will start and continue longer until there is a change in the bitcoin protocol.
This problem at the heart of the bitcoin protocol is known as “scaling.” While bitcoin miners generally agree that something needs to be done to scale, two major solutions have been proposed to address the scaling problem. Size The developers suggest either (1) reducing the amount of data required to validate each block or (2) increasing the number of transactions that each block can hold, with less data to validate per block Solution 1 will allow for faster transactions. Better and cheaper for miners. Solution 2 will deal with scaling by allowing more data to be processed every 10 minutes by increasing the block size.
In July 2017, Bitcoin miners and mining companies representing 80% to 90% of the network’s computing power voted to include a program that would reduce the amount of data required to verify each block. with solution 1
The program that voters choose to add to the bitcoin protocol is called split witness, or SegWit. The word is a combination of segregation meaning “to separate” and witness which means “to separate”. “Signatures in Bitcoin Transactions” Witness Separation means separating transaction signatures from blocks – and attaching them as extension blocks. The signature data solution is estimated to account for 65% of the data processed in each block of a transaction.
Less than a month later, in August 2017, a group of miners and developers began to fork off the bitcoin network to create a new currency based on the same codebase as cryptocurrencies. bitcoin, although the group agrees on the need for a solution to scale. But they worry that using separate witness technology won’t fully resolve the scaling problem.
Instead, they came back with a solution where the resulting 2nd currency, known as “bitcoin cash”, increased the block size to 8 MB to speed up the verification process so that it was effective around 2 million transactions per day on November 6, 2019. Cash Bitcoin is worth approx. to Bitcoin approx.